Introduction
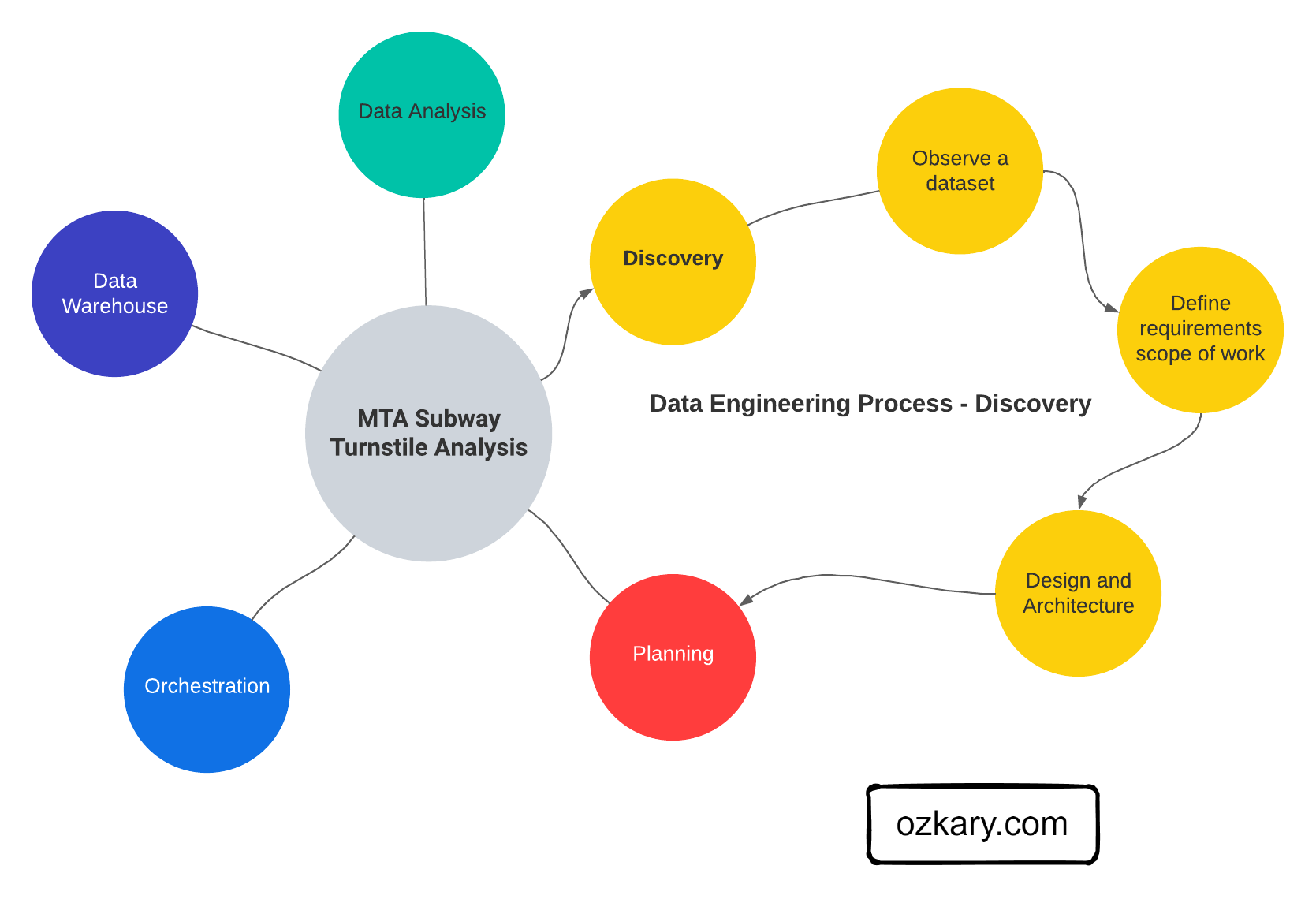
In this series of Data Engineering Process Fundamentals, we explore the Data Engineering Process (DEP) with key concepts, principles and relevant technologies, and explain how they are being used to help us deliver solutions. The first step, and important to never skip, in this process is the Discovery step.
During the discovery step of a Data Engineering Process, we look to identify and clearly document a problem statement, which helps us have an understanding of what we are trying to solve. We also look at our analytical approach to make observations about at the data, its structure and source. This leads us into defining the requirements for the project, so we can define the scope, design and architecture of the solution.
Problem Statement
A Problem Statement is a description of what it is that we are trying to solve. As part of the problem statement, we should provide some background or context on how the data is processed or collected. We should also provide a specific description of what the data engineering process is looking to solve by taking a specific approach to integrate the data. Finally, the objective and goals should also be described with information about how this data will be made available for analytical purposes.
Analytical Approach
The Analytical Approach is a systematic method to observe the data and arrive to insights from it. It involves the use of different techniques, tools and frameworks to make sense of the data in order to arrive to conclusions and actionable requirements.
Dataset Criteria
A Dataset Criteria technique refers to the set of characteristics used to evaluate the data, so we can determine the quality and accuracy of it.
In the data collection process, we should identify the various sources that can provide us with accurate and complete information. Data cleaning and preprocessing needs to be done to identify and eliminate missing values, invalid data and outliers that can skew the information. In addition, we should understand how this data is available for the ongoing integration. Some integrations may require a batch process integration at a scheduled interval. Others may require a real-time integration and/or a combination of batch and real-time processing.
Exploratory Data Analysis
We should conduct exploratory data analysis to understand the structure, patterns and characteristics of the data. We need to make observations about the data, identify the valuable fields, create statistical summaries, and run some data profiling to identify trends, metrics and correlations that are relevant to the main objective of the project.
Tools and Framework
Depending on the size and budget of the organization, the solution can be built with lots of coding and integration, or instead a low-code turn-key solution that provides enterprise quality resources could be used instead. Regardless of the approach, a programming language like Python is a popular programming language for data science and engineers, and it is always applicable. The Python Pandas library is great for data manipulation and analysis. Jupyter notes with Python scripts is great for experiments and discovery.
To run our Python scripts and Jupyter notebooks, we can use Visual Studio Code (VSCode), which is cross-platform Integrated Development Environment (IDE) tool. This tool also enables the integration with source control and deployments platforms like GitHub, so we can maintain version control and automate the deployment and test of our code changes.
To orchestrate the pipelines, we often use a workflow framework like Apache Airflow, Prefect. To host the data, we use data lakes (blob storage) and a relational data warehouse. For data modeling, incremental data and continuous test and data ingestion, Apache Spark or gbt cloud are used.
For the final data analysis and visualization, we could use tools like Looker, PowerBI and Tableau. These are tools that can connect to a data warehouse and consume the data models, so they can visualize in ways that enable stakeholders to make decisions based on the story provided by the data.
Requirements
Requirements refer to the needs, capabilities and constraints that are needed to deliver a data engineering solution. They should outline the project deliverables that are required to meet the main objectives. The requirements should include data related areas like:
- Sources and integration
- Modeling and transformation
- Quality and validation
- Storage and infrastructure
- Processing and Analytics
- Governance and Security
- Scalability and performance
- Monitoring
Design
A data engineering design is the actual plan to build the technical solution. It includes the system architecture, data integration, flow and pipeline orchestration, the data storage platform, transformation and management, data processing and analytics tooling. This is the area where we need to clearly define the different technologies that should be used for each area.
System Architecture
The system architecture is a high-level design of the solution, its components and how they integrate with each other. This often includes the data sources, data ingestion resources, workflow and data orchestration resources and frameworks, storage resources, data services for data transformation and continuous data ingestion and validation, and data analysis and visualization tooling.
Data Pipelines
A data pipeline refers to a series of connected tasks that handles the extract, transform and load (ETL) as well as the extract, load and transform (ELT) operations and integration from a source to a target storage like a data lake or data warehouse.
The use of ETL or ELT depends on the design. For some solutions, a flow task may transform the data prior to loading it into storage. This approach tends to increase the amount of python code and hardware resources used by the hosting environment. For the ELT process, the transformation may be done using SQL code and the data warehouse resources, which often tend to perform great for big data scenarios.
Data Orchestration
Data orchestration refers to the automation, management and coordination of the data pipeline tasks. It involves the scheduling, workflows, monitoring and recovery of those tasks. The orchestration ensures the execution of those tasks, and it takes care of error handling, retry and the alerting of problems in the pipeline.
Summary
The data engineering discovery process involves defining the problem statement, gathering requirements, and determining the scope of work. It also includes a data analysis exercise utilizing Python and Jupyter Notebooks ,or other tools, to extract valuable insights from the data. These steps collectively lay the foundation for successful data engineering endeavors.
Exercise - Hands-on Use Case
Since we now understand the discovery step, we should be able to put that into practice. Let’s move on to a hands-on use case and see how we apply those concepts.
👉 Data Engineering Process Fundamentals - Discovery Exercise
Thanks for reading.
Send question or comment at Twitter @ozkary
👍 Originally published by ozkary.com








0 comments :
Post a Comment
What do you think?